Programmatic Advertising Privacy: Balancing Personalization with Consumer Trust

Programmatic advertising automates the buying and selling of digital ad space, allowing brands to efficiently target audiences at scale using machine learning and real-time bidding. While this enables precise personalization, it also raises significant privacy concerns, requiring marketers to balance targeted advertising with consumer trust. Key regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and the ePrivacy Directive shape how data can be collected, stored, and used, while global privacy laws are increasingly influencing strategies worldwide.
Programmatic advertising has transformed the way brands purchase and optimize digital ad space. By leveraging automated technology, machine learning, and real-time bidding, marketers can efficiently reach specific audiences at scale.
However, as personalization strategies become more sophisticated, concerns around consumer privacy and data protection have risen to the forefront. Balancing targeted ad delivery with respect for individual privacy is essential for building trust and ensuring long-term campaign success. In this article, we explore how programmatic advertising and privacy can coexist harmoniously, offering actionable insights, best practices, and regulatory guidance for privacy-conscious marketers.
What is Programmatic Advertising?
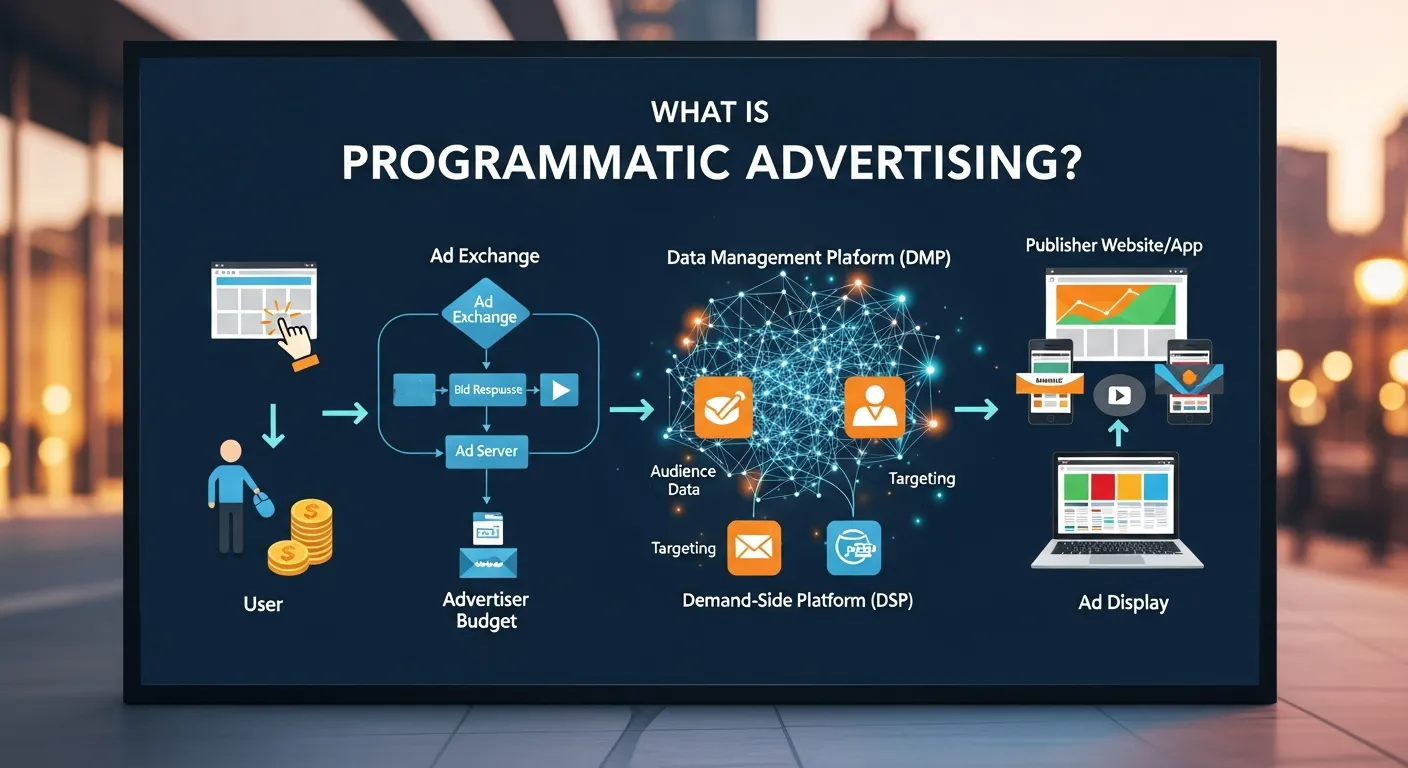
Programmatic advertising refers to the automated buying and selling of digital ad inventory through real-time bidding platforms. Instead of manually negotiating with publishers, advertisers use demand-side platforms (DSPs) to set budgets, target criteria, and optimization goals. These platforms utilize data from multiple sources, including first-party cookies, device IDs, and audience segments to display relevant ads to consumers across websites, mobile apps, and connected TV. The core advantage lies in its efficiency, precision targeting, and the ability to adjust campaigns in milliseconds based on performance data.
The Importance of Privacy in Programmatic Advertising
While programmatic technology enables highly personalized messaging, it also relies heavily on user data to inform targeting decisions. This dependence on data raises critical questions: How is consumer information collected, stored, and shared? Are users aware of how their data is being used for ad personalization? With growing concerns about data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized tracking, marketers must prioritize transparency and data protection. Ignoring privacy considerations can lead to regulatory fines, reputational damage, and decreased consumer confidence.
Key Privacy Regulations Impacting Programmatic Advertising
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation mandates explicit user consent for processing personal data within the European Union. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines.
- CCPA: The California Consumer Privacy Act grants Californian residents rights to opt out of data selling and request deletion of personal information.
- ePrivacy Directive: Also known as the Cookie Law, it requires informed consent before storing or accessing information on user devices within the EU.
- Global Privacy Laws: Countries such as Brazil (LGPD), Canada (PIPEDA), and India (DPDP) are enacting similar protections, influencing global data collection strategies.
Balancing Personalization with Consumer Trust

Trust is the cornerstone of any successful advertising relationship. To balance personalization with privacy, marketers should adopt transparent data practices. Clearly communicate data collection and usage policies through concise privacy notices and consent management platforms (CMPs). Offer consumers control over their data by providing accessible opt-in and opt-out mechanisms. Avoid excessive data collection by limiting audience segments to relevant attributes, focusing on anonymized or aggregated datasets. When consumers understand and consent to data practices, they are more likely to engage positively with targeted ads.
Best Practices for Privacy-First Programmatic Campaigns
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data needed to achieve campaign objectives, reducing the risk associated with holding large volumes of personal information.
- Consent Management: Implement CMPs that comply with GDPR and CCPA standards to capture, store, and respect user preferences.
- First-Party Data Strategies: Leverage data directly gathered from customer interactions, such as CRM systems and email subscriptions to maintain quality and consent integrity.
- Contextual Targeting: Use contextual signals like page content, keywords, or topics to serve relevant ads without relying on personal user data.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic privacy audits to ensure compliance with evolving regulations and internal data governance policies.
Technology Solutions to Enhance Privacy
Several technology solutions can help advertisers uphold privacy standards while maintaining campaign effectiveness. Privacy-preserving identity solutions such as Unified ID 2.0 replace third-party cookies with encrypted user identifiers that respect user consent. Secure multiparty computation enables encrypted data collaboration between brands and publishers without exposing raw personal data. Additionally, privacy-focused analytics platforms anonymize user behavior insights, allowing marketers to measure performance without compromising individual privacy.
Integrating Programmatic Advertising with Omnichannel Strategies
Programmatic advertising does not exist in isolation—it works best as part of a broader omnichannel marketing strategy. By integrating programmatic campaigns with email marketing, social media, content marketing, and offline channels, brands can create a seamless customer experience. For example, programmatic ads can reinforce messages delivered via email campaigns or support awareness generated through social media content. Synchronizing campaigns across channels also allows marketers to collect richer first-party data, improve audience segmentation, and maintain consistent messaging while respecting privacy preferences. The key is to ensure that data shared across channels is consented to and handled securely to maintain consumer trust.
Challenges and Risks in Privacy-First Programmatic Advertising
While privacy-first programmatic strategies offer long-term benefits, they also present unique challenges. The deprecation of third-party cookies limits traditional targeting methods, making it harder to reach some audiences effectively. Implementing consent management platforms and anonymized tracking solutions requires technical expertise and investment. There is also a risk of over-anonymizing data, which can reduce the granularity of insights and limit campaign optimization. Additionally, brands must remain vigilant about evolving regulations in multiple jurisdictions, as non-compliance can result in fines and reputational damage. Mitigating these risks involves continuous monitoring, staff training, and adopting technologies that balance privacy with actionable insights.
Ethical Considerations in Programmatic Advertising
Ethics are increasingly central to programmatic advertising. Beyond simply complying with regulations, brands must evaluate the societal and psychological impacts of their campaigns. Practices such as hyper-targeting vulnerable populations, exploiting sensitive personal data, or using manipulative consent tactics (dark patterns) can damage consumer trust and harm a brand’s reputation. Ethical programmatic advertising emphasizes transparency, fairness, and accountability, ensuring that personalization does not come at the cost of consumer well-being.
Key Ethical Practices for Programmatic Advertising:
- Establish internal guidelines for responsible data usage.
- Ensure diversity in algorithmic decision-making to avoid bias.
- Prioritize consumer well-being alongside campaign performance.
- Maintain transparency in data collection and targeting strategies.
By embedding these principles, marketers not only protect their brand but also foster trust, which is critical for programmatic advertising strategies for success.
Leveraging First-Party Data for Competitive Advantage
With the phase-out of third-party cookies, first-party data has become a cornerstone of successful programmatic campaigns. Brands can collect data directly from customer interactions such as website visits, email subscriptions, purchases, and loyalty program participation. When analyzed responsibly and with proper consent, first-party data allows advertisers to create highly personalized programmatic advertising campaigns while minimizing privacy risks.
Best Practices for Using First-Party Data:
- Collect data through opt-in interactions such as website forms, apps, and loyalty programs.
- Analyze data via Data Management Platforms (DMPs) or Customer Data Platforms (CDPs).
- Use insights to enhance targeting accuracy and campaign performance.
- Strengthen customer trust and loyalty by respecting personal information.
First-party data not only improves targeting precision but also supports programmatic advertising SEM strategy and cross-channel integrations, including programmatic TV advertising work and other programmatic-advertising strategies for success.
Compliance and Privacy Management in Programmatic Advertising
Responsible programmatic advertising also involves strict compliance with data privacy regulations. Brands must balance personalization with consumer trust, ensuring campaigns are legally compliant while delivering relevant messages.
Core Compliance Guidelines:
- Follow GDPR, CCPA, and local privacy regulations.
- Encrypt sensitive customer data and restrict access.
- Clearly communicate data collection practices to consumers.
- Regularly audit platforms for compliance and ethical alignment.
Privacy, Ethics, and Data Strategies in Programmatic Advertising
| Focus Area | Strategy | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ethical Advertising | Avoid hyper-targeting vulnerable groups; ensure algorithmic fairness; transparent consent | Builds consumer trust and protects brand reputation |
| First-Party Data | Collect data from website visits, email subscriptions, purchases, loyalty programs; use DMPs/CDPs | Enhances targeting accuracy and campaign ROI |
| Privacy Compliance | Follow GDPR, CCPA, and local laws; encrypt and secure data; manage opt-ins | Reduces legal risk and strengthens consumer confidence |
| Transparency | Clearly inform consumers about data collection and usage | Improves user engagement and loyalty |
| Consumer-Centric Approach | Balance personalization with ethical practices; monitor campaign impact | Promotes responsible programmatic advertising and long-term trust |
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Privacy-First Advertising
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly important role in programmatic advertising, especially in privacy-first approaches. AI algorithms can help anonymize user data, identify patterns without exposing personal identifiers, and optimize campaigns in real time. Machine learning can also predict audience behavior based on aggregated datasets, reducing the need for invasive tracking. Furthermore, AI can automate compliance monitoring, alerting marketers to potential privacy violations and helping ensure campaigns adhere to regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. By leveraging AI responsibly, brands can achieve both high-performance targeting and strong privacy safeguards.
Consumer Education and Transparency as a Marketing Strategy

Educating consumers about data collection, usage, and privacy protections is becoming a key differentiator in programmatic advertising. Brands that clearly communicate how they handle personal data, offer transparent consent options, and explain the benefits of personalized ads can build stronger trust with their audiences. This transparency can be integrated into marketing campaigns, privacy policies, and consent management tools. When consumers understand the value exchange—how sharing certain information leads to more relevant and helpful advertising—they are more likely to engage positively. Ultimately, prioritizing consumer education and transparency not only supports compliance but also enhances brand loyalty and long-term campaign effectiveness.
Measuring Success: KPIs for Privacy and Performance
Traditional programmatic KPIs such as click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, and cost per acquisition (CPA) remain important. However, privacy-first campaigns should also track metrics that reflect consumer trust and compliance. Consider measuring opt-in rates, consent withdrawal rates, and user satisfaction through post-campaign surveys. Monitor data usage errors or policy violations to identify potential privacy risks early. By combining performance metrics with privacy indicators, brands can optimize campaigns holistically and demonstrate a commitment to responsible data stewardship.
The Future of Privacy and Programmatic Advertising
The programmatic ecosystem is evolving rapidly with the deprecation of third-party cookies, increased regulation, and consumer demand for privacy. Marketers will need to adopt alternative targeting methods such as cohort-based approaches like Google Privacy Sandbox, and invest in clean room partnerships for secure data collaboration. Artificial intelligence will play a greater role in anonymizing data and automating compliance checks. Ultimately, brands that proactively embrace privacy as a strategic advantage will build stronger consumer relationships and achieve sustainable advertising success. Programmatic advertising offers unparalleled efficiency and precision, but it also brings privacy responsibilities. By understanding key regulations, adopting privacy-first technologies, and prioritizing transparency, marketers can deliver personalized experiences without eroding consumer trust. The future of programmatic lies in finding the optimal intersection between performance and privacy. As the digital landscape continues to shift, maintaining this balance will be critical for brands aiming to build resilient, consumer-centric advertising strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is programmatic advertising?
Programmatic advertising is the automated buying and selling of digital ad space using technologies like demand-side platforms (DSPs) and real-time bidding. It allows advertisers to target specific audiences precisely, optimize campaigns in real-time, and increase efficiency in media buying.
2. How does programmatic advertising use consumer data?
Programmatic campaigns use data from sources such as first-party cookies, device IDs, CRM systems, and audience segments. This information helps advertisers deliver relevant ads to the right audience at the right time while optimizing campaign performance.
3. Why is privacy a concern in programmatic advertising?
Since programmatic advertising depends heavily on collecting and processing user data, it raises concerns about consent, transparency, and data security. Mishandling this information can lead to regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and a loss of consumer trust.
4. What are the key privacy regulations affecting programmatic advertising?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU mandates explicit user consent for processing personal data. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) allows residents to opt out of data selling and request deletion of their personal information. The ePrivacy Directive, also known as the Cookie Law, requires informed consent before storing or accessing information on user devices in the EU. Additionally, countries like Brazil (LGPD), Canada (PIPEDA), and India (DPDP) are introducing similar privacy protections that affect global advertising strategies.
5. How can brands balance personalization with privacy?
Brands can achieve balance by being transparent about how data is collected and used. They should implement consent management systems to capture user preferences, limit data collection to only what is necessary, and provide clear options for users to opt in or out. Using anonymized or aggregated data for targeting also helps ensure privacy while delivering personalized experiences.
6. What are some best practices for privacy-first programmatic campaigns?
Advertisers should focus on collecting only the data needed to achieve campaign objectives, ensure consent management complies with GDPR and CCPA, leverage first-party data from CRM systems and subscriptions, and use contextual targeting based on page content or topics rather than personal data. Regular audits should be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with privacy policies and regulations.
7. Which technologies support privacy in programmatic advertising?
Technologies such as privacy-preserving identifiers like Unified ID 2.0 replace third-party cookies with encrypted IDs that respect user consent. Secure multiparty computation allows brands and publishers to collaborate on data without exposing raw personal information. Privacy-focused analytics platforms enable advertisers to measure campaign performance while anonymizing user behavior data.
8. How should advertisers measure the success of privacy-first campaigns?
In addition to traditional performance metrics such as click-through rate, conversion rate, and cost per acquisition, privacy-first campaigns should track consent rates, opt-out rates, user satisfaction, and incidents of policy violations. Evaluating both performance and trust ensures campaigns are effective while maintaining consumer confidence.
9. What does the future hold for programmatic advertising and privacy?
The programmatic landscape is evolving due to the phasing out of third-party cookies, stricter privacy regulations, and rising consumer expectations. Marketers are likely to adopt cohort-based targeting approaches, invest in clean room partnerships for secure data collaboration, and use AI to anonymize data and automate compliance processes. Brands that embrace privacy proactively will gain a strategic advantage and build stronger consumer relationships.
10. Can programmatic advertising succeed without violating privacy?
Yes, programmatic advertising can be effective while respecting privacy. By using transparent data practices, relying on first-party or anonymized data, and leveraging privacy-enhancing technologies, marketers can deliver personalized campaigns that build trust and comply with regulatory standards.
Learn more…New to the concept of automated ad buying? Don’t miss our full breakdown on Best Books on Programmatic Advertising to Level Up Your Skills .





